Internet has a lot of information about the LED display construction, however, in our opinion, it is not always comprehensive and inconvenient for the reader. We have prepared several articles in order to contribute to the topic: In this article you will learn the basics, in article «LED modules and cabinets» you will learn LED screen components and in article «LED screen control systems» you will be respectively introduced to control systems.
So, the LED screen (also called LED display, video screen, LED panel, etc.) is a high-tech product, containing a large number of components complying with complex operating principles based on LEDs. LEDs constitute pixels, pixels are integrated into modules, modules are placed in cabinets which make up the LED screen.
LED (light-emitting diode) is a semiconductor that lights up when electricity passes through it. LEDs do not contain filaments as conventional light bulbs, and they do not have fine details that can be broken or burned, as a result, their lifespan is long. LED color: red, white, green, etc depends on the type of semiconductor crystal. If we change the chemical composition of the crystal, the color changes. Usually the LED casing is painted in order to know the LED color without turning it on.
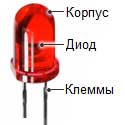
LED is the smallest element according to size, but not according to its importance. In many ways the cost of the LED screen depends on the cost of a single LED. LED high quality models can cost several times more than those with similar technical characteristics. Today the most quality model is produced by Japanese manufacturer Nichia, slightly lower rating have Cree LEDs produced in the USA. Next are Samsung and Epistar (Taiwan) have about the same cost, Chinese Absen, Silan multicolor and some others have lower price. Usually LED screens use Chinese Silan LEDs. They are relatively low in price and have a long lifespan.
Standard LEDs operate for 100,000 hours (11+ years) of continuous use and their life cycle is not affected by the number of on / off cycles. LED Brightness named technique of pulse width modulation (PWM) is regulated as follows: the voltage across the LED is not constant, but alternating. Depending on what brightness is required, current supply time is determined, i.e. if you need half the brightness, the voltage is half the time of the refresh rate.
Refresh rate (refresh rate, Refresh) is the number of updates (measured in Hz). For example, if a computer display's refresh rate is 100 Hz, it means that the image update occurs 100 times per second. This characteristic is very important because the image quality depends on it. If the refresh rate is not sufficient, image flickering will be visible due to the way the human eye perceives light. If flickering is quick, the light is summed up and is perceived constantly. Today refresh frequency in LED screens is not less than 600 Hz, often this is enough.
LEDs are the real unsung heroes in electronics. They do dozens of different jobs and are found in all kinds of devices. Among other things, they form the numbers on digital clocks, and indicate that the appliances are turned on. Basically, LEDs are just tiny light bulbs that fit easily into an electrical circuit. One or more of LEDs form a pixel.
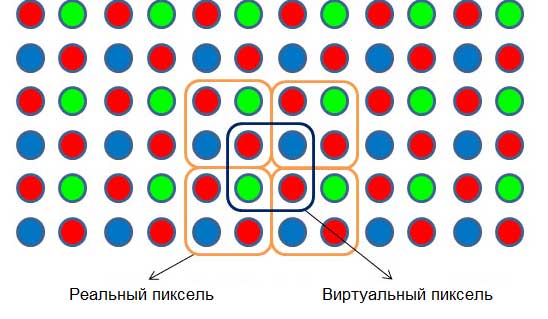
Pixel is a glowing point and the smallest unit of an image. To create a whole variety of colors three types of LEDs of different colors are used: red, green and blue (namely R, G and B, respectively). To create larger pixels, the diameter of which can reach up to 80 mm (used in LED screens for media facades), the number of LEDs is increased, for example: 2R1G1B - ie 2 red, 1 green and 1 blue. LEDs quantity and color is determined based on the best white balance. Quality white color will only be present when red, green, and blue are in ratio 1: 4.6: 0.16. Deviations from this ratio will result in white color deviations, such as bluish white or yellowish-green.
LED Screen Resolution is the number of pixels per 1 m2 of the LED screen. The optimal resolution for the screen 4m wide and 3m high is a resolution of at least 256x192, ie 256 pixels horizontally and 192 vertically. This resolution is achieved with a 15.6 mm pixel pitch.
Pixel pitch is the distance from the center of one pixel to the center of the neighboring pixel. Accordingly, the larger the pitch, the lower the screen resolution. Pixel pitch is determined by latin letter "P", for example, P6 - means LED screen with a 6 mm pixel pitch.
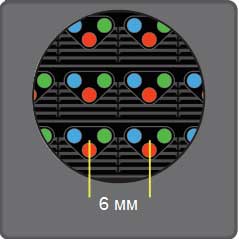
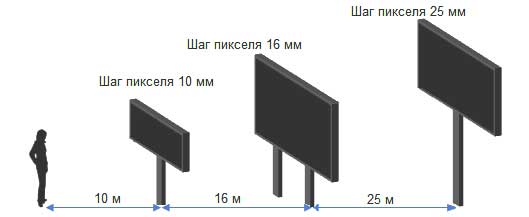
Considering the LED screen construction: selecting a pixel pitch is very important: a pitch reduction by only a couple of millimeters significantly increases the density of light-emitting diodes and as a result - screen resolution. Necessary pixel pitch can be estimated as follows: it is directly proportional to the recommended viewing distance, ie, the screen with a pixel pitch of 10 mm. It is recommended to be viewed from 10 meters distance, the screen with a pixel pitch of 16 mm - 16 meters, 25 mm - 25 meters. If the distance is smaller, the viewer is able to distinguish individual pixels, if bigger – details will not be visible. Accordingly, in order to determine pixel pitch you need to know the distance of the predominant part of the audience from the LED screen.
There are several ways of combining LEDs into pixels called pixel configuration. Today two main types: DIP and SMD.

DIP configuration - is the principle of implantation of each diode on the circuit board in its own body. Because one pixel is formed by a series of LEDs, the overall reliability of the screen brightness increases.
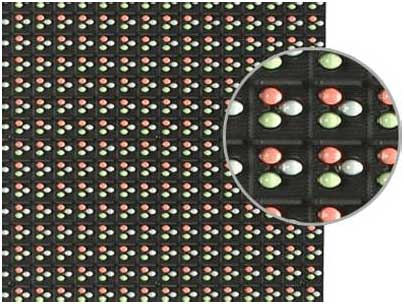
DIP configuration modules are often used for outdoor LED screens, they have high brightness and an enhanced mask for protection against mechanical damage and are resistant to low temperatures, moisture and dust. In addition, they have good color stability and use virtual pixel technology, which allows forming a so-called "virtual pixel" - it does not exist physically, but it creates the illusion of presence for the human eye. As a result, it is possible to improve sharpness and make the image more detailed and realistic. The disadvantages of DIP modules include a small viewing angle.
The viewing angle is an angle within which the viewer observes the image brightness by 50% to 100%. The maximum brightness will be observed if the screen is viewed perpendicularly. DIP configuration screens have a viewing angle of 120 degrees horizontally and 60 degrees vertically, while SMD configuration - 120 degrees horizontally and 120 vertically.
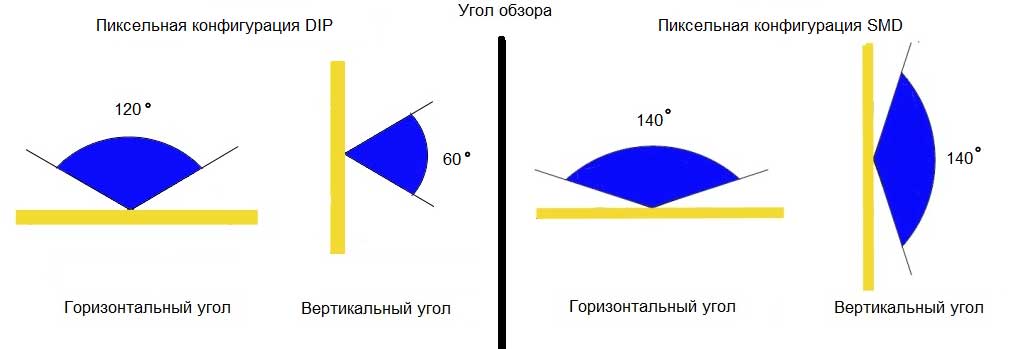
SMD configuration. This is the latest development greatly effected on LED screen technology. Its distinctive feature is that three different LED colors are combined in one body, sometimes the colors are named RGB (3 in 1). SMD technology provides a better and accurate color reproduction. It is usually used for indoor LED screens with a small pixel pitch - concert and sports halls, television studios, train stations and airports. SMD configuration pixels tend to have a lower brightness, about 1200-3000 cd / m2, compared to DIP configuration pixels (6000-10000 cd / m2), but they are sufficient for indoor, otherwise viewers will be blinded. They have a lower power consumption, they are thinner, and therefore lighter, they have good color stability, a wide viewing angle, rich palette of colors. In the recent years, this technology has spread to outdoor LED screens.

LED installed in the circuit board using DIP and SMD technology form a LED module, this topic will be further developed in another article: «LED modules and cabinets».
